Understanding Generators: Does a Generator Produce AC or DC Current?
Generators play a crucial role in our daily lives, providing power in various applications. One common question that often arises is whether a generator produces alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). In this blog post, we will delve into the inner workings of generators, exploring the fundamental principles that govern their operation and shedding light on whether the output is AC or DC.
The Basics of Generator Operation
To comprehend the type of current a generator produces, it's essential to grasp the basic principles of its operation. At its core, a generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in a conductor. In a generator, this is achieved by rotating a coil of wire within a magnetic field.
Types of Generators
Before we dive into the specifics of AC and DC output, let's briefly explore the two main types of generators: AC generators (alternators) and DC generators.
AC Generators (Alternators)
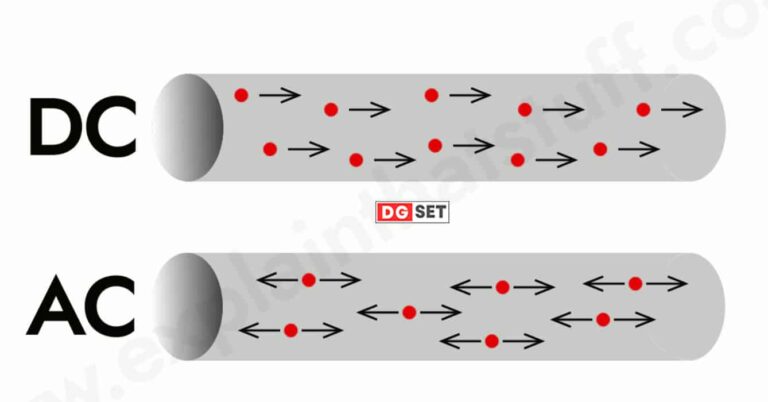
AC generators, commonly known as alternators, are widely used to produce alternating current. In an alternator, a rotating coil within a magnetic field induces an alternating voltage in the coil. This alternating voltage results in an oscillating current flow, constantly changing direction.
DC Generators
DC generators, on the other hand, produce direct current. These generators employ a commutator—a rotary switch that reverses the current direction in the coil windings, ensuring a unidirectional (direct) current output.
Does a Generator Produce AC or DC Current?
Now that we've covered the basic principles and types of generators, let's answer the central question: Does a generator produce AC or DC current?
AC Output in Most Generators
The majority of generators, especially those used in power generation and distribution systems, produce alternating current. AC has several advantages, including ease of voltage transformation and efficient long-distance power transmission. Therefore, generators that supply electricity to homes, businesses, and the grid are typically AC generators.
DC Output in Specialized Generators
While AC generators are more prevalent, there are instances where generators produce direct current. These generators are often used in specific applications where a constant and unidirectional flow of electricity is required.
Examples of DC Generators
Battery Charging Generators: Some generators are designed to charge batteries, delivering a direct current to store electrical energy for later use.
Electrochemical Processes: Generators used in electrochemical processes, such as certain industrial applications and laboratories, may produce DC current to facilitate specific reactions.
Factors Influencing the Type of Output
Several factors influence whether a generator produces AC or DC current. Understanding these factors provides insights into the design and application of generators.
Application Requirements
The primary factor determining the type of current generated is the application's requirements. If the end-use demands a constant and unidirectional flow of electricity, a DC generator is chosen. In contrast, applications that benefit from alternating current, such as most household appliances, lighting systems, and industrial machinery, are powered by AC generators.
Efficiency and Transmission
AC generators are favored for long-distance power transmission due to their efficiency in voltage transformation. Transformers can easily convert AC voltages to higher or lower levels, making AC the preferred choice for electricity distribution across the grid. DC transmission over long distances faces higher energy losses, limiting its practicality for widespread use.
Cost and Complexity
The cost and complexity of generator design also play a role. AC generators are often simpler and more cost-effective for widespread use, making them the default choice for most power generation applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the type of current produced by a generator depends on its design, application, and the specific requirements of the end-use. While the majority of generators produce alternating current, there are specialized instances where direct current generators find their niche.
Understanding the nuances of generator operation and the type of current they generate is essential for engineers, technicians, and anyone interested in the fascinating world of electrical power generation. Whether it's the hum of an alternator providing electricity to homes or the precision of a DC generator in a laboratory setting, generators play a pivotal role in shaping our modern world.
Does a Generator Produce AC or DC Current: FAQs Answered!
Does every generator produce alternating current (AC)?
No, not every generator produces alternating current. While the majority of generators, especially those used in power distribution, generate AC, there are specialized generators designed to produce direct current (DC). The type of current a generator produces depends on its design, application, and the specific requirements of the end-use.
What is the primary application of generators producing direct current (DC)?
Generators that produce direct current (DC) find applications in scenarios where a constant and unidirectional flow of electricity is required. Common uses include battery charging generators and applications involving electrochemical processes, such as certain industrial processes and laboratory experiments.
Why are alternating current (AC) generators more common in power distribution systems?
AC generators are more common in power distribution systems due to their efficiency in voltage transformation. Alternating current can easily be transformed to higher or lower voltages using transformers, making it the preferred choice for long-distance power transmission. AC's efficiency in voltage transformation, coupled with lower energy losses during transmission, makes it practical for widespread use.
Are there instances where a generator can produce both AC and DC simultaneously?
Yes, some generators can produce both AC and DC simultaneously. These are known as dual-output generators and are designed to cater to applications that require both types of current. Dual-output generators often have separate windings or circuits to generate AC and DC, providing versatility for diverse electrical needs.
What factors influence the choice between AC and DC generators in specific applications?
Several factors influence the choice between AC and DC generators, including the specific requirements of the application, efficiency considerations, and the cost and complexity of generator design. Applications demanding a constant and unidirectional flow of electricity often favor DC generators, while those benefiting from alternating current, such as household appliances and industrial machinery, typically use AC generators.
Can generators be modified to change their output from AC to DC or vice versa?
While it's theoretically possible to modify generators to change their output from AC to DC or vice versa, such modifications are complex and often impractical. The design and internal components of a generator are optimized for a specific type of output. Converting the output type would require significant alterations to the generator's structure and components, making it a challenging and costly endeavor.
Are there any advantages of using direct current (DC) generators in specific applications?
Yes, there are advantages to using DC generators in specific applications. DC generators provide a constant and unidirectional flow of electricity, making them suitable for applications such as battery charging and electrochemical processes. Additionally, DC generators can offer precise control over voltage and current levels, making them valuable in certain industrial and laboratory settings.
How do generators contribute to the overall electricity supply chain?
Generators are essential components in the electricity supply chain. They convert various forms of energy, such as mechanical or chemical energy, into electrical energy. Generators play a crucial role in power plants, providing the electricity that is then transmitted through the grid to homes, businesses, and industries. They are foundational to the process of generating and distributing electrical power on a large scale.
Generator maintenance: click here to read our blog