How Does a Generator Work When the Power Goes Out: A Comprehensive Guide

In times of power outages, generators play a crucial role in providing electricity to homes and businesses. But have you ever wondered how a generator works when the power goes out? In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the inner workings of generators, focusing on their functionality during power outages.
Understanding Generators
Generators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They consist of various components working together to generate electricity. When the power from the grid goes out, generators serve as backup power sources, ensuring that essential appliances and systems remain operational.
Types of Generators
There are several types of generators available, including portable generators, standby generators, and whole-house generators. Each type has its own set of features and capabilities, but they all function on the same basic principles.
How Generators Work During Power Outages
When the power goes out, generators spring into action to provide electricity. The process can be summarized in the following steps:
- Fuel Combustion: Generators typically run on diesel, gasoline, natural gas, or propane. When the power goes out, the generator's engine starts by burning fuel to produce mechanical energy.
- Mechanical Energy Conversion: The mechanical energy produced by the engine is then transferred to an alternator or generator head. This component converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through the principle of electromagnetic induction.
- Voltage Regulation: The electrical energy produced by the generator is initially in the form of alternating current (AC). Voltage regulation mechanisms ensure that the output voltage remains stable and within acceptable limits.
- Power Distribution: The generated electricity is then transmitted through the generator's outlets or connected to the home or building's electrical system through a transfer switch. This enables the powered appliances and systems to draw electricity from the generator.
- Automatic Operation (for Standby Generators): Standby generators are equipped with automatic transfer switches that detect power outages and automatically start the generator. Once the grid power is restored, the transfer switch seamlessly switches back to the grid and shuts down the generator.
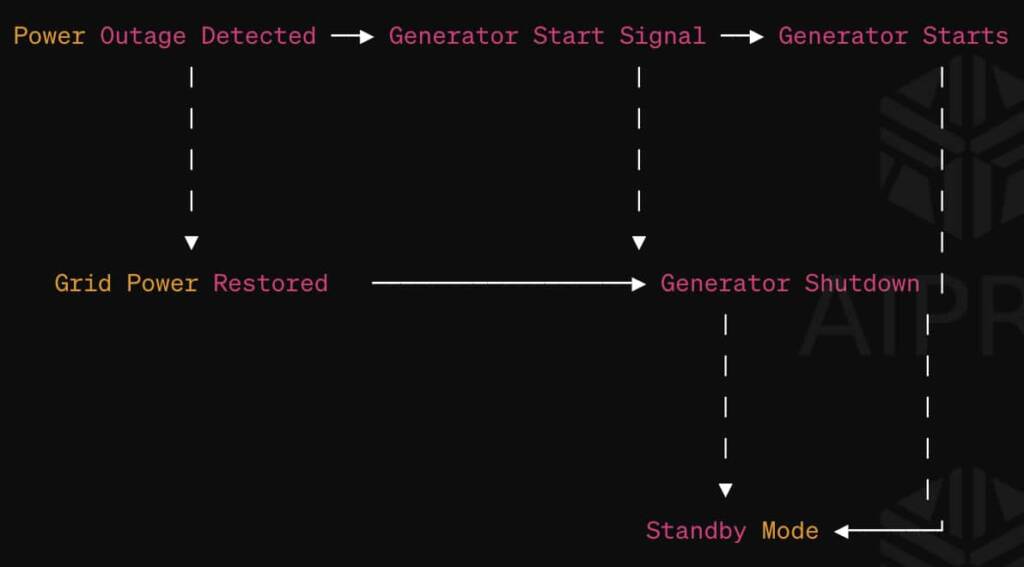
Flowchart illustrating how a generator works when the power goes out
Below is a simplified flowchart illustrating how a generator works when the power goes out:
- Power Outage Detected
- Grid power is interrupted due to an outage.
- Generator Start Signal
- The automatic transfer switch detects the power outage.
- Sends a signal to start the generator.
- Generator Starts
- The generator engine initiates.
- Fuel (gasoline, diesel, propane, natural gas) is combusted.
- Mechanical Energy Production
- The engine converts fuel's chemical energy into mechanical energy.
- Alternator Functionality
- Mechanical energy drives the alternator or generator head.
- The alternator produces alternating current (AC) electricity.
- Voltage Regulation
- Voltage regulators maintain stable voltage output.
- Ensures electricity remains within acceptable limits.
- Power Distribution
- Electricity travels through generator outlets or connection points.
- Distributed to appliances, lights, and other systems.
- Appliance Power On
- Powered appliances and systems function normally.
- Critical devices like refrigerators, lights, and HVAC systems stay operational.
- Automatic Transfer Switch Monitoring
- Continuously monitors grid power status.
- Grid Power Restored
- Once grid power is restored, the transfer switch detects it.
- Sends a signal to stop the generator.
- Generator Shutdown
- Generator engine shuts down.
- Electrical load is transferred back to grid power.
- Standby Mode
- Generator returns to standby mode, ready for the next power outage.

Benefits of Generators During Power Outages
Generators offer several benefits during power outages, including:
- Continuous Power Supply: Generators ensure that critical appliances such as refrigerators, lights, and medical equipment remain operational during outages.
- Comfort and Convenience: With a generator, homeowners can maintain a comfortable indoor environment by powering heating and cooling systems.
- Business Continuity: For businesses, generators are essential for preventing disruptions to operations and minimizing financial losses during power outages.
- Safety and Security: Generators provide security by keeping security systems, alarms, and communication devices powered, enhancing safety during emergencies.
Conclusion
Generators play a vital role in providing backup power during power outages, ensuring that homes and businesses remain functional and secure. Understanding how generators work when the power goes out can help homeowners and businesses make informed decisions about selecting and maintaining these essential devices. Whether it's a portable generator for occasional use or a standby generator for continuous power backup, generators offer peace of mind and reliability when the grid fails.
FAQs About How Generators Work When the Power Goes Out
- How does a generator work when the power goes out?
When the power from the grid goes out, a generator springs into action by burning fuel (such as diesel, gasoline, natural gas, or propane) in its engine. This combustion process produces mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then transferred to an alternator or generator head, which converts it into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. The generated electricity is then regulated for voltage stability and distributed through the generator's outlets or connected to the home/building's electrical system via a transfer switch.
- What types of fuel do generators use during power outages?
Generators can run on various types of fuel, including diesel, gasoline, natural gas, and propane. The choice of fuel often depends on factors such as availability, convenience, and the specific requirements of the generator.
- What is the difference between portable generators and standby generators during power outages?
Portable generators are designed for temporary use and are manually started during power outages. They are typically smaller in size and capacity, suitable for powering essential appliances and devices. Standby generators, on the other hand, are permanently installed and automatically start when they detect a power outage. They are larger and more powerful, capable of providing backup power to entire homes or businesses for extended periods.
- How do standby generators automatically start during power outages?
Standby generators are equipped with automatic transfer switches (ATS) that monitor the utility power supply. When the ATS detects a power outage, it sends a signal to the generator to start automatically. Once the generator is running and producing electricity, the ATS switches the electrical load from the grid to the generator. When grid power is restored, the ATS transfers the load back to the grid and shuts down the generator.
- Can generators be used indoors during power outages?
Portable generators should never be used indoors or in enclosed spaces due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Generators emit exhaust gases that contain carbon monoxide, which can be deadly if inhaled in high concentrations. It is essential to place portable generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from doors, windows, and vents.
- How long can a generator provide power during a power outage?
The runtime of a generator during a power outage depends on several factors, including the generator's fuel capacity, load demand, and maintenance. Generators with larger fuel tanks or connections to external fuel sources can provide power for longer durations. Additionally, managing the electrical load and performing regular maintenance can optimize the generator's runtime during outages.
- Can generators be used to power sensitive electronic devices during power outages?
Yes, generators can be used to power sensitive electronic devices during power outages. However, it is essential to use a generator with clean power output and voltage regulation mechanisms to prevent damage to electronics. Additionally, using surge protectors and voltage regulators can further safeguard sensitive devices from power fluctuations.
- How do generators contribute to safety and security during power outages?
Generators enhance safety and security during power outages by keeping essential systems and appliances powered. This includes security systems, alarms, communication devices, lighting, and medical equipment. By ensuring continuity of power, generators help maintain a safe and secure environment, especially during emergencies or natural disasters.
- Are there any maintenance requirements for generators during power outages?
Yes, regular maintenance is essential to ensure the reliable operation of generators during power outages. This includes periodic inspections, oil and filter changes, fuel system checks, and testing of automatic transfer switches (for standby generators). Following the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule helps identify and address potential issues before they impact generator performance during outages.
- How do generators contribute to business continuity during power outages?
Generators play a crucial role in maintaining business continuity during power outages by ensuring uninterrupted operations. Businesses rely on generators to power essential equipment, servers, communication systems, and security devices, minimizing downtime and financial losses. With backup power from generators, businesses can continue serving customers, maintaining productivity, and safeguarding critical operations during outages.


